Hi this is
Anjaneya Vadivel, Every time I make a website I usually try to plan my classes out ahead of time in a regular text file, this small step will reduce the amount of time spent figuring out how to design my application considerably. I find this especially useful when working with CodeIgniter. I can even create all the files ahead of time, (usually I use the touch command in terminal to do it quickly).
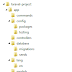
This is how my template might look before being filled out :
Example Class Template
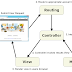
MODEL: (classes with functions to GET/INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE from the database, called from controller classes)
model_class.php
[some functions listed here]
CONTROLLER: (functions to handle user requests : call model functions and load up views)
class_a.php
[some functions listed here]
class_b.php
[some functions listed here]
VIEW: (PHP files that contain the necessary html to see the page, loaded from controller classes)
template/html_head.php
template/html_tail.php
Example Blog Class Template
Once again this is not a completed template below as the functions would usually be filled in with as much information as I can plan before starting the actual application. This means thinking of all parameter names, and the insides of the functions before starting.
MODEL:
posts_model.php
get_posts()
get_post_by_id()
get_tags_by_post_id()
insert_post()
update_post_by_id()
delete_post_by_id()
etc…
CONTROLLER:
posts.php
index()
etc
pages.php
index($page)
etc…
VIEW:
template/html_head.php
template/html_tail.php
post/single_view.php
post/multi_view.php
page/contact_us
page/home
etc…
Why plan?
If you don’t already create a template to help organize your thoughts when programming, you should try it! It’s the easiest way to see the amount of work that needs to be done, divide work among multiple people easily, and help make MVC programming a little more intuitive.
How much planning do you do before starting your application?